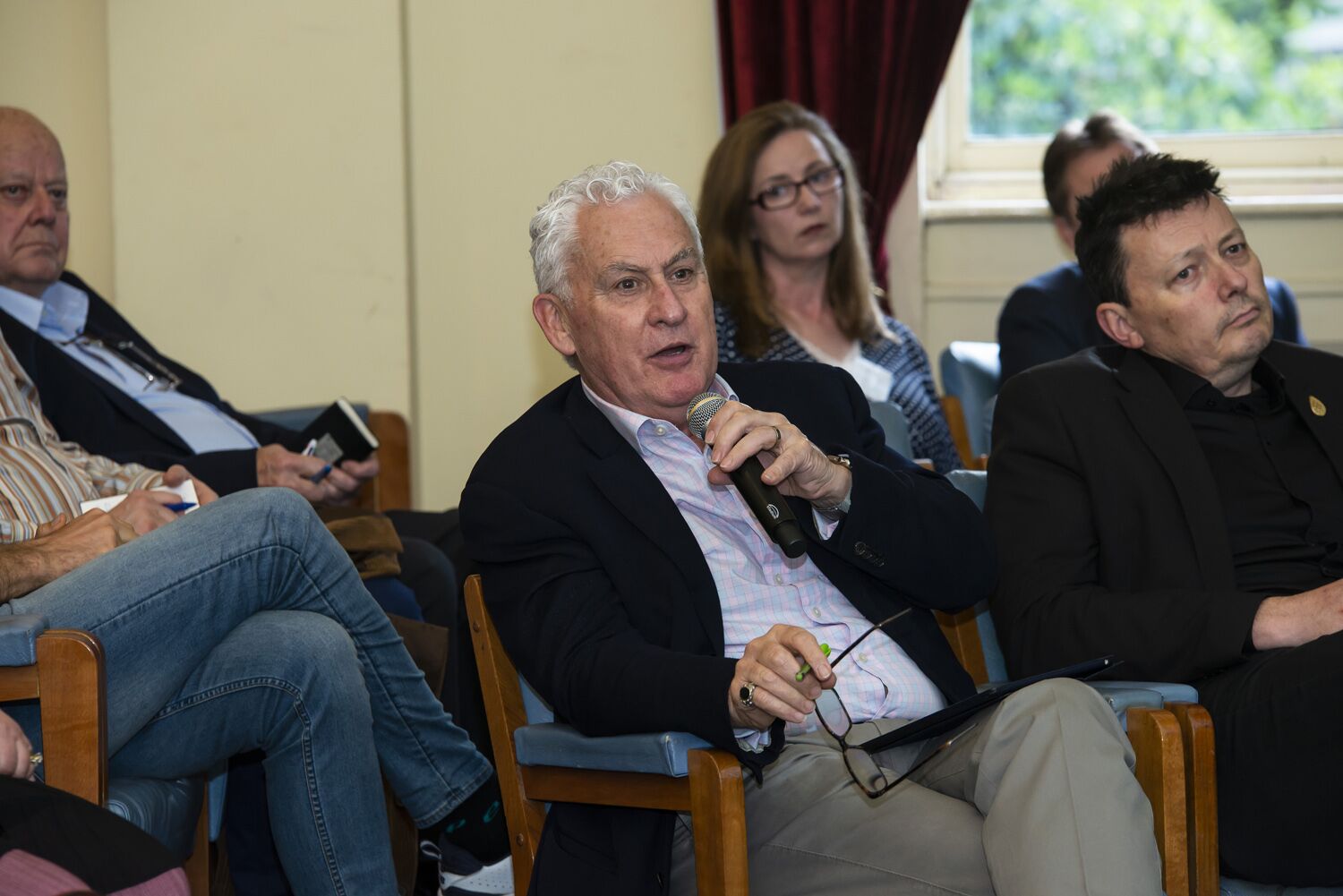
Air pollution can alter the regulation of immune systems, stunt lung development, and increase blood pressure, demonstrating that even at a young age, human immune, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems are negatively impacted by exposure. Even before birth, the growth, development, and overall health of unborn babies is impacted. So what can we do about it?
Continuing to invest in sustainable industrial techniques will be extremely important in improving the environment and our relationship with it. “Green chemistry” seeks to minimise or eliminate the use or generation of hazardous substances. One of the goals of green chemistry is for the term to completely disappear – it should simply become how we practise chemistry, and make things.
The WHO estimates that one in six people will experience infertility in their lifetime. Further, we have seen a dramatic decrease of almost 50% in both male sperm count and female conception rates in the past 50 years. This decrease can be largely attributed to our increasing exposure to chemicals in our environment known as Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals.
When we think of pollution in streams and rivers, we tend to think first of rubbish in water; the litter traps along the Yarra River in Melbourne’s CBD that are often overflowing, or the empty plastic bottles along the Moonee Ponds Creek. But water pollution takes many forms, from physical trash to invisible chemicals that accumulate in our waterways.
Victoria can simultaneously solve Melbourne’s future sewerage crisis whilst building a sustainable carbon credits sector. A common sight for Melbourne’s residents in the 1850’s would have been carts full of “nightsoil” trundling down Flemington Road. Melbourne subsequently built one of the world’s best municipal water systems, supporting the quality of life its residents enjoy today.